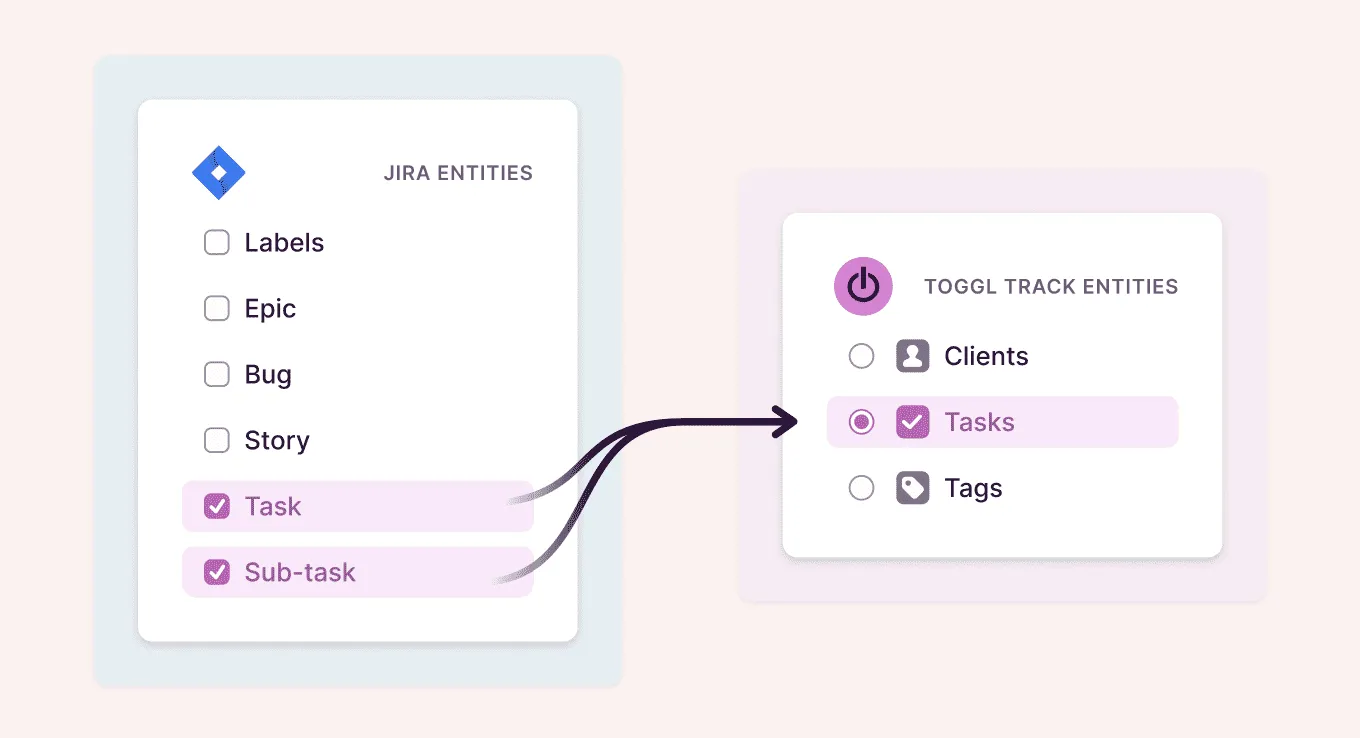
What is Tarantula Jira Integration?
Tarantula Jira integration is the process of connecting Tarantula, a bug tracking tool, with Jira, a popular project management and issue tracking software. This integration allows teams to synchronize data, streamline workflows, and improve collaboration between different departments or teams. By linking these two powerful tools, organizations can create a more unified and efficient system for managing software development, testing, and other projects. The integration facilitates the seamless transfer of information between Tarantula and Jira, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the most up-to-date information, thus leading to better decision-making and faster project completion. The integration leverages APIs and other technologies to establish a continuous data flow, minimizing manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors. This enables project managers, developers, and testers to work in a more coordinated and productive manner, ultimately enhancing the overall efficiency of the development lifecycle.
Benefits of Using Tarantula with Jira
Integrating Tarantula with Jira offers a multitude of advantages, significantly enhancing project management and software development processes. The integration ensures that bug reports, test results, and other critical information are readily accessible within the Jira environment. This real-time synchronization eliminates the need for manual data transfer, thus reducing errors and saving valuable time. Improved visibility into the development process is another key benefit, as all stakeholders, including project managers, developers, and testers, can track the status of issues and bugs in a centralized location. This visibility fosters better communication and collaboration, ultimately leading to faster issue resolution and more effective project delivery. Additionally, this integration promotes data-driven decision-making by providing comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities. The ability to generate customized reports and track key performance indicators (KPIs) allows project teams to identify trends, assess team performance, and make informed decisions to improve project outcomes.
Streamlined Issue Tracking
Streamlined issue tracking is a major advantage of integrating Tarantula with Jira. Bugs found in Tarantula can be automatically synced to Jira, creating a single source of truth for all issues. This seamless data flow eliminates the need to manually create issues in Jira based on reports from Tarantula, saving time and reducing the chance of errors. The integration allows the automatic transfer of all relevant information, such as bug descriptions, screenshots, and severity levels, to the corresponding Jira issue. By consolidating issue data in a unified platform, teams gain better visibility into the bug resolution process. This enhanced visibility enables faster identification and resolution of issues, leading to reduced development cycles and improved software quality. Integrated issue tracking promotes collaboration among team members, and enables efficient communication and tracking of bug fixes.
Improved Collaboration
Integrating Tarantula with Jira greatly enhances team collaboration. The synchronization of data ensures that everyone, from developers to testers and project managers, is working from the same information. This reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings and miscommunication, fostering a more cohesive team environment. Real-time updates on bug statuses, test results, and other relevant information are immediately accessible to all authorized users within Jira. This enables team members to stay informed about the progress of issues and the overall project status. Team members can easily share information, provide feedback, and collaborate on solutions, all within a unified platform. This integrated approach to collaboration promotes better communication, quicker issue resolution, and a more efficient workflow, resulting in improved team productivity and project outcomes. The ability to easily see the status of each bug and the assigned resources ensures a coordinated response.
Enhanced Reporting and Analytics
One of the significant benefits of Tarantula Jira integration is the ability to generate more comprehensive and insightful reports and analytics. The consolidated data from both platforms allows for the creation of detailed reports on bug trends, project progress, and team performance. With readily available data, project managers can easily track key metrics such as the number of open issues, the average time to resolution, and the overall quality of the software. This data-driven approach provides valuable insights that can be used to improve the efficiency of the development process and make informed decisions. Custom reports can be generated to meet the specific needs of different teams and stakeholders. Such insights help to identify bottlenecks, assess the effectiveness of testing processes, and optimize resource allocation, all of which lead to better project outcomes and improved software quality. The ability to analyze historical data to predict future trends is a valuable asset.
Step-by-Step Setup Guide for Tarantula Jira Integration
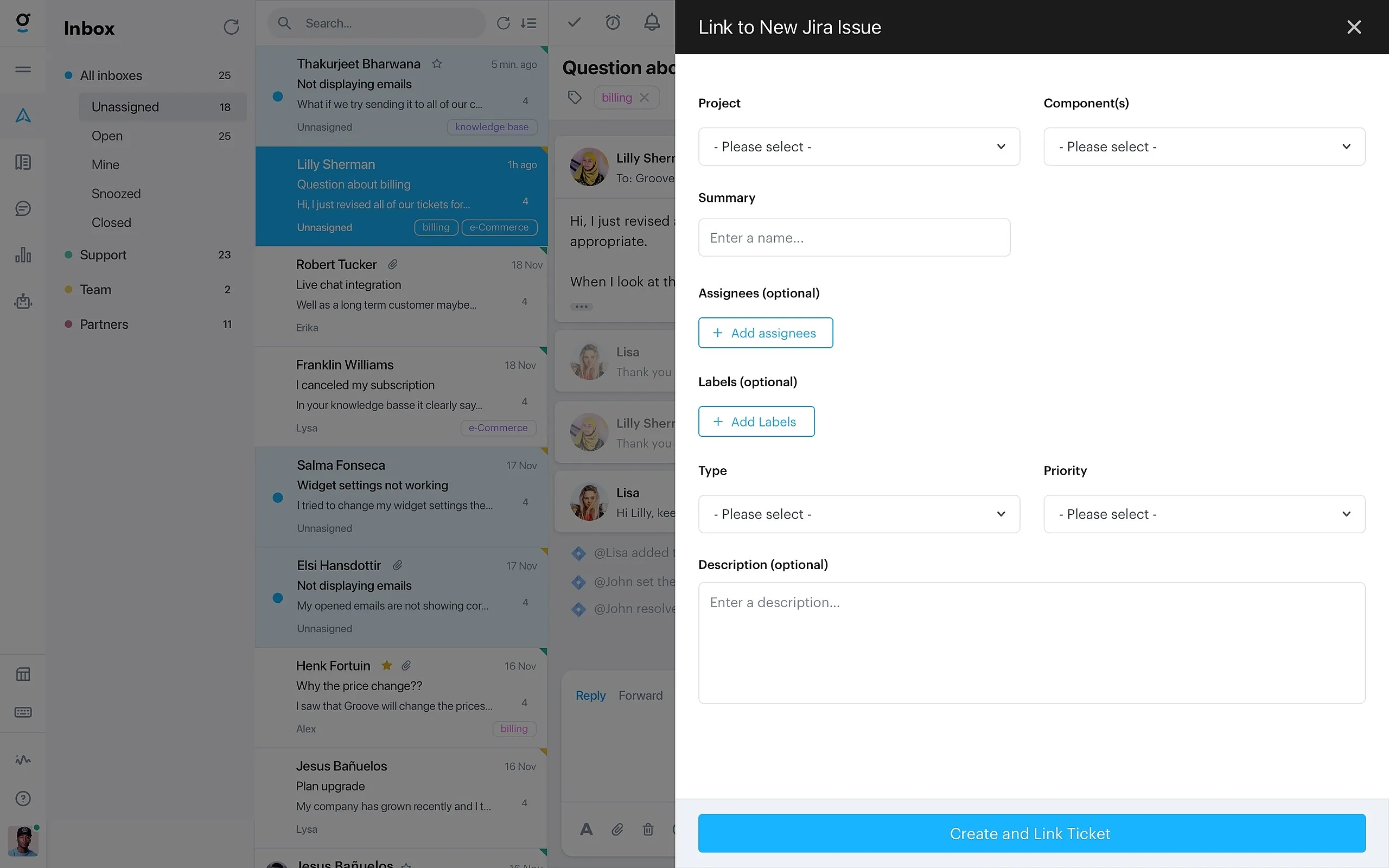
Setting up the Tarantula Jira integration involves several key steps. Start by ensuring you have the necessary access permissions to both Tarantula and Jira. Next, determine the specific integration method you’ll use, which may involve using a plugin, API, or a third-party tool. Each method will have its own set of prerequisites. For the plugin approach, you’ll often need to install and configure the plugin within your Jira instance. If utilizing an API, you may need to create API keys and configure authentication settings. Third-party tools offer pre-built integrations but may involve additional costs. Ensure that both systems are compatible, and that the versions of Tarantula and Jira you are using are supported by the chosen integration method. After selecting an integration method, configure the connection settings, including the URLs and authentication details for both Tarantula and Jira. This setup phase involves entering the necessary credentials and mapping the data fields between the two systems. Carefully review the settings to confirm that data synchronization is configured properly and that data flows seamlessly between the two platforms.
Prerequisites and Requirements
Before beginning the Tarantula Jira integration, it’s essential to ensure that all the necessary prerequisites and requirements are in place. Firstly, you will need active accounts and administrative access to both Tarantula and Jira. This is crucial for installing plugins, configuring settings, and managing the data synchronization process. Ensure that you have the correct version of both Tarantula and Jira, and that they are compatible with each other. Review the documentation for the integration method you have chosen to ensure your versions are supported. You should also ensure that your network setup allows for seamless communication between the two systems. This may involve configuring firewalls and other security measures. If you are using a plugin, you should check that your Jira instance has sufficient resources to support it. Make sure you have all the required software libraries and dependencies installed. For API-based integrations, you’ll need to generate API keys, and ensure you have an understanding of how these are handled. Verify that your existing infrastructure meets the demands of the data flow, considering bandwidth and server capabilities. Checking these prerequisites in advance will help you avoid potential complications during the integration.
Installing and Configuring Tarantula
The installation and configuration of Tarantula is a critical step in preparing for the Jira integration. Begin by downloading the Tarantula software package from a reliable source and following the vendor’s installation instructions. This will typically involve running a setup wizard that guides you through the installation process. During installation, you may need to select installation directory. Once Tarantula is installed, you will need to configure it by accessing its settings or control panel. This may include setting up user accounts, defining project settings, and configuring the database connection. Ensure you configure any security settings. Next, test the basic functionality of Tarantula to make sure it is working correctly. This involves creating test cases, logging bugs, and verifying that the system can generate reports as expected. After verifying that Tarantula works independently, move on to configuring it for integration with Jira. This generally involves enabling API access or installing any necessary plugins. It’s also crucial to configure the settings for the data to be transferred between systems. Thoroughly review the configuration to ensure it is set up correctly before proceeding.
Connecting Jira to Tarantula

Connecting Jira to Tarantula involves establishing a link that allows these two systems to communicate and exchange data. The precise steps depend on the chosen integration method. For plugin-based integrations, you typically install the plugin within Jira and then configure it with the connection details for your Tarantula instance. This usually involves entering the URL of your Tarantula server and providing authentication credentials. For API-based integrations, you will need to configure Jira to use the Tarantula API. This might involve generating API keys, defining authentication methods, and specifying how data will be exchanged between systems. Regardless of the method, it is important to configure how data fields will be mapped from Tarantula to Jira. When you have entered all of the required details, save the connection settings and test the connection. Once the connection is established, verify the data flow by attempting to synchronize data between the two systems. Ensure that bugs logged in Tarantula appear in Jira, and that any relevant information, such as severity levels and descriptions, is accurately transferred. It may be necessary to review logs or troubleshoot errors to resolve any connectivity issues.
Configuring Issue Synchronization
Configuring issue synchronization is the core of the Tarantula Jira integration, determining how bug reports and other data are transferred between the two systems. This typically involves defining which fields from Tarantula will be mapped to corresponding fields in Jira. For example, the bug description from Tarantula should map to the description field in Jira, while the bug’s status maps to the status field. You’ll need to configure the synchronization direction, specifying whether issues will flow from Tarantula to Jira, or vice versa. Some integrations support bi-directional synchronization, where changes made in either system are reflected in the other. You might be able to specify triggers or events that initiate synchronization. This could be based on the creation of a new bug in Tarantula, or when the status of an issue is changed. You can also set up filters to control which issues are synchronized. This ensures that only relevant data is transferred between systems. Testing the synchronization configuration is crucial to ensure that data is transferred correctly and that fields are mapped as expected. This testing phase is necessary to identify and resolve any issues before deploying the integration to a production environment.
Advanced Configuration Options
Beyond the basics, advanced configuration options allow for customization and optimization of the Tarantula Jira integration. One advanced feature is the ability to configure custom fields. You can define the mapping of custom fields between the two systems, ensuring all specific data is accurately transferred and visible in both platforms. Another aspect is the configuration of synchronization rules, where you can define conditions or rules that govern how data is synchronized. This includes options to filter which issues are synchronized, or to trigger synchronization based on certain events or conditions. Advanced logging and auditing options are available to provide greater visibility into the integration process. This includes the ability to track synchronization activities, identify errors, and troubleshoot issues. You can also configure options for handling attachments. This includes defining how to sync attachments, such as screenshots or documents, between both tools. Advanced configuration also allows you to schedule synchronization tasks to ensure regular and automated data updates. Implementing these advanced options can improve the efficiency and reliability of your Tarantula Jira integration.
Customizing Field Mappings
Customizing field mappings is a critical component for successful data synchronization between Tarantula and Jira. This process ensures that data fields in both systems are accurately aligned, preventing inconsistencies and ensuring that all relevant information is readily accessible. Field mapping configuration allows you to establish a direct correspondence between fields in Tarantula and Jira. For instance, you would map the ‘bug description’ field in Tarantula to the ‘description’ field in Jira. Consider the data types of each field. The field mapping process also involves configuring how data types, such as dates, numbers, and text strings, are handled when synchronized. This includes formatting options and data transformation. You can also define default values for specific fields when data is transferred. This helps prevent empty or null values in Jira. It’s essential to map custom fields. If your systems use custom fields, define these mappings to make sure that all necessary information is synchronized. Regularly review and update your field mappings to accommodate changes in your project or data requirements. Proper field mapping significantly improves data accuracy and ensures teams can seamlessly work together with synchronized information.
Automating Data Synchronization
Automating data synchronization between Tarantula and Jira streamlines the integration process and guarantees that data remains consistent across both platforms. This ensures that information flows between the tools without manual intervention, enhancing efficiency and reducing the potential for human error. Automating data synchronization eliminates the need to manually trigger updates. It enables a continuous, real-time flow of information. The primary methods for automating data synchronization are often based on scheduled tasks or triggers. Scheduled tasks involve configuring the integration to synchronize data at regular intervals, like every hour or every day. Triggers can be event-based. For example, when a new bug is logged in Tarantula, or when the status of an issue changes, the system automatically updates Jira. You may also be able to schedule the synchronization during off-peak hours to minimize performance impacts. Review and test your automated synchronization setup regularly. Proper automation ensures teams always have up-to-date information, thus promoting effective collaboration and reducing manual data entry.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Troubleshooting common issues is an integral part of maintaining a stable and reliable Tarantula Jira integration. Connection problems are among the most frequent challenges. These issues can often result from network problems, incorrect configurations, or authentication errors. Check the connection settings, verify that the URLs are correct, and confirm that the correct credentials are being used. Synchronization errors are another major issue. These arise when data transfer fails for various reasons, such as invalid data, field mapping conflicts, or system-level problems. Review error logs to identify the cause of the issue, and address any data inconsistencies. Data synchronization failures can be caused by issues with the API. When errors occur, it’s crucial to assess the configuration of the integration method you’re using. In case of plugin-based solutions, ensure the plugin is updated. For API integrations, verify that API keys are valid and that the API endpoints are responding correctly. Regularly test the integration, review logs, and monitor the synchronization process to quickly resolve any issues. These efforts improve the reliability and functionality of the integration.
Connection Problems
Connection problems between Tarantula and Jira can hinder data synchronization and disrupt workflows. Connection issues may arise from incorrect server addresses, authentication problems, or network connectivity issues. The first step in troubleshooting is to verify the server URLs for both Tarantula and Jira are correct and accessible. Ensure that there are no typos, and that the servers are running and reachable on your network. Next, check authentication credentials. Confirm that the username, password, and API keys used for the integration are valid, and that the account has sufficient privileges in both systems. Review firewall settings. Confirm that the firewalls or network security measures do not block communication between the two platforms. Network connectivity issues, such as DNS resolution problems, or network outages can also cause connection problems. You might want to use tools such as ping or traceroute to test network connectivity. Review any recent changes to the network infrastructure or settings that might be affecting the connectivity. Keeping these best practices in mind is essential to minimize downtime and ensure reliable data synchronization.
Synchronization Errors
Synchronization errors can prevent the seamless transfer of data between Tarantula and Jira, leading to information gaps and inefficiencies. Data inconsistencies, invalid data types, and incorrect field mappings are among the common causes of these errors. To begin troubleshooting, review the error logs for the integration. Logs often contain specific error messages, that pinpoint the source of the problem. Then verify that the data types of fields are compatible between both systems. For example, an integer field in Tarantula should be mapped to an integer field in Jira. If field mappings are misconfigured, correct these mappings to ensure data is mapped correctly. Additionally, test the integration to ensure errors are not reoccurring. Investigate the integration method for any issues, such as plugin updates. By addressing these issues, you can minimize synchronization errors and ensure a smooth data flow between Tarantula and Jira, promoting better collaboration and more reliable project management.
Optimizing Tarantula Jira Integration
Optimizing the Tarantula Jira integration enhances performance, improves efficiency, and maximizes the value you derive from the integration. Regularly review and refine your field mappings to ensure that they are accurate, efficient, and reflect any changes in your projects or data structure. Remove unnecessary fields and mappings. Fine-tune the synchronization frequency. Adjust the synchronization intervals based on your project requirements. Evaluate the performance of your integration periodically. This includes assessing the data transfer speed, error rates, and any impact on system resources. Review the integration setup and configuration regularly, and update as necessary. Consider advanced features such as API caching or data compression, which can increase the speed of your integration. Implementing these optimization strategies leads to a more streamlined workflow and improves the overall effectiveness of your Tarantula Jira integration.
Best Practices for Data Management
Data management best practices are essential to the success of your Tarantula Jira integration. Implement a consistent naming convention for fields and data entries in both systems, to reduce confusion and ensure consistency. Regularly back up data. Create a backup strategy to protect your data from any loss. Data security is crucial. Secure your Tarantula and Jira instances by using strong passwords, enabling encryption, and restricting access to sensitive data. Review and maintain the integrity of your data. Regularly check data for inconsistencies or errors. Monitor the data synchronization process to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of data transfers. By adhering to these data management best practices, you ensure a more streamlined integration and optimize data quality.
Enhancing Team Workflow
Enhancing team workflow through the Tarantula Jira integration is essential for maximizing productivity and collaboration. Ensure team members are well-trained on how to use both Tarantula and Jira, and how the integration works. Establish clear communication channels for sharing information and discussing issues. Create templates and workflows to streamline repetitive tasks. Encourage teams to use the integrated platform. Regularly review and refine your processes to ensure they are efficient and user-friendly. Actively solicit feedback from team members to identify areas for improvement and address any concerns. Using these strategies improves the workflow. By streamlining the bug reporting, tracking, and resolution processes, you improve efficiency.
Conclusion
The Tarantula Jira integration offers a potent solution for teams aiming to enhance their bug tracking and project management workflows. By seamlessly synchronizing data between these two platforms, businesses can streamline issue tracking, improve collaboration, and optimize project outcomes. The step-by-step guide details the process, from setup and configuration to the crucial steps of troubleshooting and optimization. Through an understanding of the integration’s benefits, a solid understanding of how to configure the setup, and a commitment to data management best practices, organizations can harness the full potential of this integration. Regular maintenance, user training, and a focus on continuous improvement are critical to ensuring the integration continues to meet evolving project needs, ultimately driving greater efficiency and success in software development and project management. The power to effectively manage projects and resolve issues efficiently, resulting in improved outcomes and increased team productivity.